Overview
Many of our backup solutions utilize Windows 'volume shadow copy' (VSS) writers to perform backups. VSS provides the functionality to take a snapshot of a volume, allowing backups to backup data from the unchanging snapshot instead of the volume that is changing all the time. This technology is available on Windows XP, Vista, Server 2003 (or better) operating systems. On older operating systems it will still try to backup open files when possible, and then will check after a file has been backed up to make sure it was not modified while being backed up.
Determine if VSS is the issue:
1. Open an elevated command prompt.
- Click the Start button.
- In the search box, type cmd.
- Right-click on cmd.exe and choose Run as Administrator. If done properly, the below User Account Control window will appear.
- Click Yes to run the Windows Command Prompt as Administrator.
2. Type the following command and press enter: vssadmin list writers
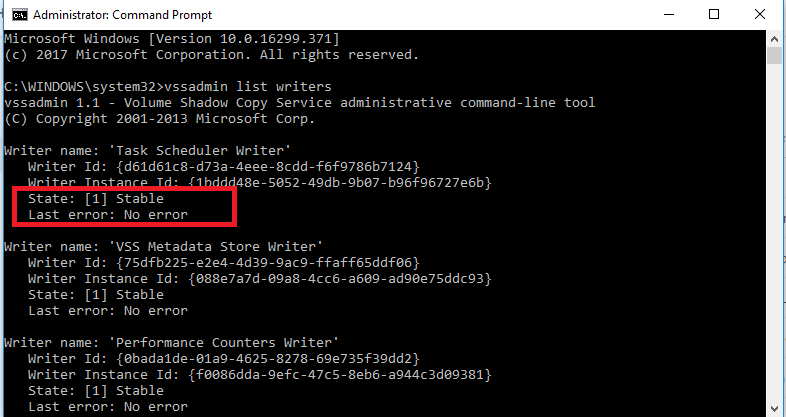
3. Ensure the writers all show ‘Stable’ with ‘No Error’, like this:
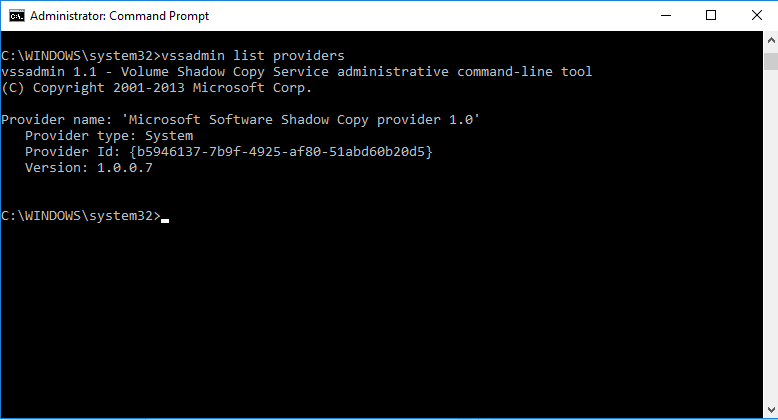
4. Type the following command and press enter:
vssadmin list providers
Microsoft should be the only provider, unless you are actively using the backup associated with another provider listed. Most products prefer to be the only backup solution installed, and many will not run properly with two VSS providers installed. Please uninstall any other provider present if possible. If you find another provider, but you don’t have another backup solution installed any longer, please skip to step 6.
Troubleshooting
If VSS troublshooting is necessary, use the numbered guide below to help make the fix as simple and quick as possible, ruling out simple fixes before moving on to more in-depth, difficult fixes.
After each step, please check your VSS writers again as described above. If they are stable with no error, then try your backup again. If they are not stable with no error, move on to the next step, testing again after each step.
1. If the writers are not stable, reboot your protected machine.
If the writers are stable, please continue to Step 2.
Computers that have not been rebooted in a while may cause VSS to malfunction. VSS writers in a failed state can often be brought to a stable state simply by rebooting.
If the machine cannot be rebooted any time soon, or it is necessary to continue troubleshooting immediately, without rebooting, you may be able to reset the writers to a stable state by restarting some services:
- COM+ Event System
- COM+ System Application Service
This may not be started (if not, start it)
- Distributed Transaction Coordinator Service
- Volume Shadow Copy Service
If possible, please also restart the affected VSS writer service. (For example, Virtual Server 2005 VSS writer or the Hyper-V VM manager Service to the Hyper-V VSS writer.)
Please be aware that other dependent services will be restarted with these services. Please be sure none of the dependent services will affect your particular environment negatively before restarting each service.
Check the writers again (vssadmin list writers). If there are no errors on any writers listed, attempt a backup. If the writers are not stable, or they go into a failed state after trying the backup again, you will need to reboot the protected system.
If the writers are stable, but you still get VSS errors on the backup, continue troubleshooting below:
2. Check the fragmentation and verify a chkdsk does not need to be run.
Due to everything that happens during a VSS backup, it is important to have an operating system running smoothly. If there is abnormal delay during the backup process, the backup may timeout and fail. A fragmented drive, or a drive that needs repaired with a chkdsk can cause backups to fail.
If you’re not familiar with what actually happens during a VSS snapshot, here is a link describing all the things that happen during a VSS :
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa384589(v=VS.85).aspx
a. If you are seeing more than 10% fragmentation, use your favorite defragmentation tool, and then try the backup again.
b. If you have disk errors that require a chkdsk repair, please run:
chkdsk /f /r
This command will ensure that any issues found are repaired, if possible.
3. Check the Event Viewer for any additional error information logged by that VSS writer.
Ensure that Microsoft does not have any specific resolution for any errors present related to the VSS error
4. Clear any existing shadows.
VSS has a limit on the number of snapshots that can be kept on the system; furthermore, these snapshots take up space on the drive that is needed to take these snapshots. The following will clear this space.
NOTE: If the shadows are in use (such as when you right click and select restore previous versions), this will no longer be possible as those versions will be lost.
- Open an elevated command prompt (like above).
- Enter vssadmin delete shadows /all.
This will clean up the VSS snapshots. Some improperly configured systems accumulate hundreds of VSS snapshots that persist in the system. - Enter vssadmin list writers and check for errors.If writers are stable, attempt a backup. If there are any writers that are listed as Failed or have an error, start troubleshooting from Step 1 again.
5. Ensure VSS shadow storage has sufficient space.
VSS has a limit to the amount of space that is set to keep and take snapshots by default. Sometimes the default value 5% of the total size of the volume is not large enough. Please run the following command to set the size to have no limit.
To check the shadowstorage size:
- vssadmin Resize ShadowStorage /For=<DRIVE LETTER> /On=<DRIVE LETTER> /MaxSize=UNBOUNDED
example: vssadmin Resize ShadowStorage /For=C: /On=C: /MaxSize=UNBOUNDED
- On systems running a desktop operating system, the above command is the only way to set the size of the VSS Snapshot save location. On Windows Server Operating systems, the GUI can be used:
- Open Disk Management diskmgmt.msc
- Right Click on the First Volume
- Select Properties
- Select the Shadow Copies Tab
- Select The First Disk in the List
- Select Settings
- Select No Limit
- Click OK
6. If you don't get any VSS writer errors when using vssadmin list writers, but the system isn't able to create a new VSS snapshot (and you have deleted all existing snapshots):
a. Check to see if other backup tools are present. Some backup solutions can conflict with each other, causing VSS errors.
b. Then, open the Registry Editor (regedit) as an administrator and check the following branch to ensure there are no non-Microsoft providers present:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\VSS\Providers
If possible, uninstall any other solution present.
c. If you do find another provider, it may be a residual registry entry from a previous backup software installation. You can save the entry by exporting the entire registry to a file (right click and select Export) and then it's safe to delete the entire branch entry underneath the non-Windows vss provider.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\VSS\Providers.
NOTE: Before making any changes to the registry, please export a copy of the registry to a memorable location so you can re-import it if necessary.
d. Reboot and run vssadmin list writers to confirm the problem has been resolved.
- If writers are stable, attempt a backup.
- If there are any writers that are listed as Failed or have an error, start troubleshooting from Step 1 again.
7. If the PC or server you are using is a virtual machine host, you need to install the latest VMware Tools (for VMware), Virtual Machine Additions (Virtual Server), and integration tools (Hyper-V) on each virtual machine.
8. If you have completed all the above noted steps and you are still getting either VSS errors or unable to complete a snapshot, it will be necessary to contact Microsoft Technical Support, as the issue is related to a malfunction within VSS or the Windows operating system.